UI / UX Design
Training Smarter, Not Harder: Redesigning Onboarding for India’s Rail Engineers
Built a VR simulation using Meta Quest 2 that cut training time and made safety drills more real—without the risks
Year :
2025
Industry :
AR/VR
Client :
Indian Railways
Project Duration :
6 months



Project Summary
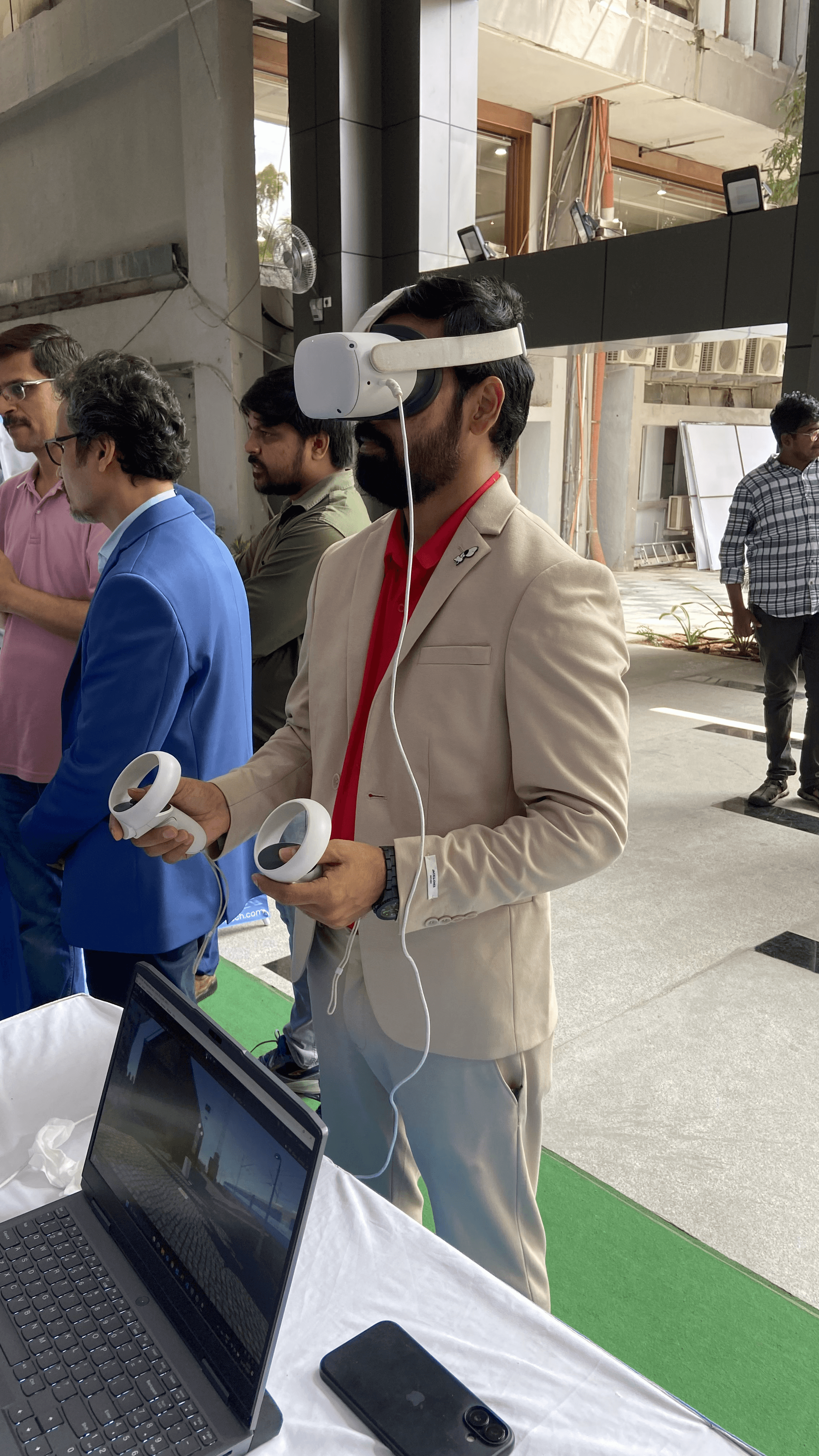
Indian Railways wanted to replace costly, travel-heavy classroom sessions with an immersive VR program that lets new engineers practise safety procedures and equipment handling in a lifelike but risk-free setting. I served as VR Experience Designer for a six-month pilot, partnering with a small squad of VR developers and railway domain experts. The result is a Quest 2-based simulation that blends gaze-driven teleport navigation, optional hand-tracking controls, structured tutorials, and real-time feedback to prepare recruits for real locomotives.



The Challenge
Cost & Scale – Training 1.5 lakh staff on physical simulators costs ₹350 cr and requires 47 decentralised centres.
Safety – Live drills around rolling stock expose novices to hazards such as high-voltage OHE lines and moving bogies.
Accessibility – Early user tests showed many trainees struggled with twin joysticks and long sessions triggered motion sickness.
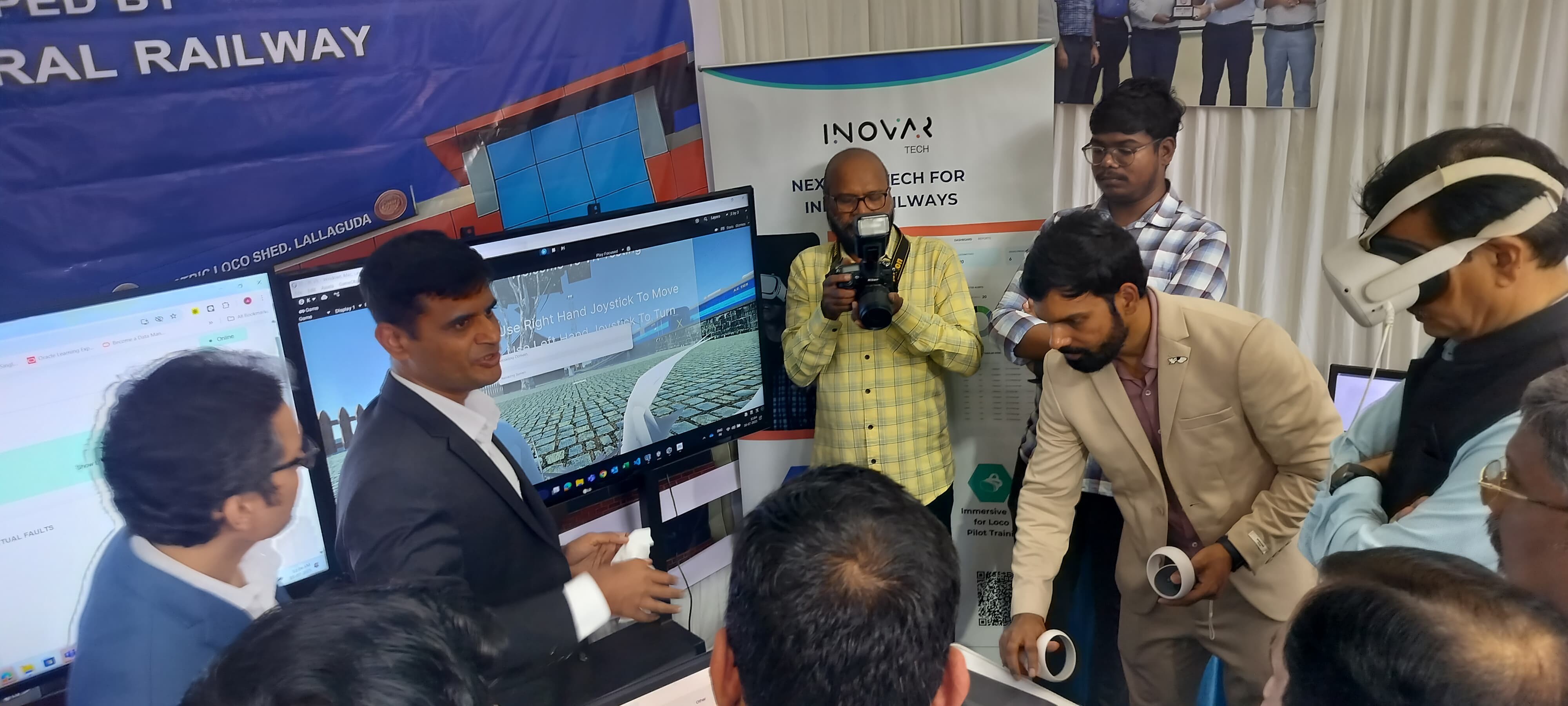





My Role & Team
Responsibility | Contribution |
|---|---|
UX Strategy | Defined learning goals, success metrics, and interaction model |
Research Lead | Ran contextual inquiry inside training sheds and conducted 18 semi-structured interviews |
Interaction Design | Prototyped locomotion, menu, and feedback systems in Unity |
Usability Testing | Led three iterative play-tests with 28 participants |
I collaborated daily with two Unity developers, one 3D artist, and two senior training officers from the Kurla Car Shed.
User Research & Needs
Methods: field observation in maintenance sheds, think-aloud VR prototypes, and task analyses.
Key Insights
Low Controller Literacy – Only 22% of recruits had prior VR exposure; joystick “thumb drift” slowed task completion by 18 s on average.
Critical Recall Moments – Trainees must memorise sequences (e.g., pantograph isolation) under time pressure. Static videos failed to build muscle memory.
Motion Comfort – Continuous locomotion triggered nausea in >40% of novices; teleportation reduced adverse reports to 7%.
VR Design Approach
Locomotion & Navigation
Gaze-assisted teleportation with arc pointers keeps optical flow near zero to curb VR sickness.
Room-scale interaction inside engine compartments for tasks demanding fine manipulation (e.g., replacing brake pads).
Interaction Model
Hand-Tracking 2.2 on Quest 2 enables natural pinches and grabs for users who find controllers intimidating.
Context-sensitive affordances: interactive parts glow on proximity to reduce cognitive load.
Onboarding & Comfort
Five-minute guided tutorial introduces safety bubble boundaries, teleport mechanics, and comfort menu.
Dynamic vision modulator narrows peripheral FOV during rapid movement to mitigate motion sickness.
Accessibility toggles for seated mode, high-contrast UI, and language localisation (HI, EN).
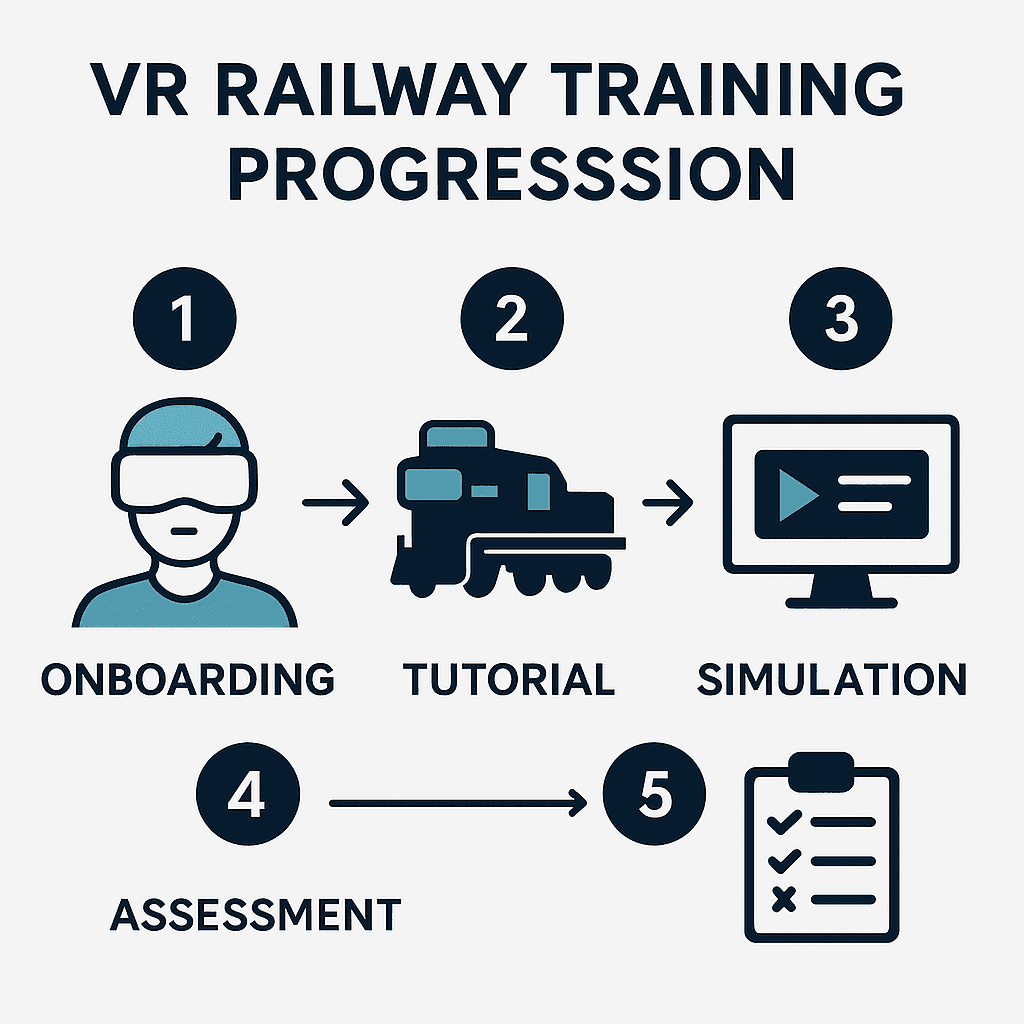
Learning Progression
Observe – Cinematic 360° briefing.
Practise – Step-by-step scaffold with ghost-hand guidance.
Assess – Timed scenario without hints; scoring on accuracy, safety, and time.
Feedback Systems
Spatial audio cues for hazard warnings.
HUD badge meter tracking errors and remaining steps.
Post-scenario heat-map replay pinpointing missteps for instructor debriefs.
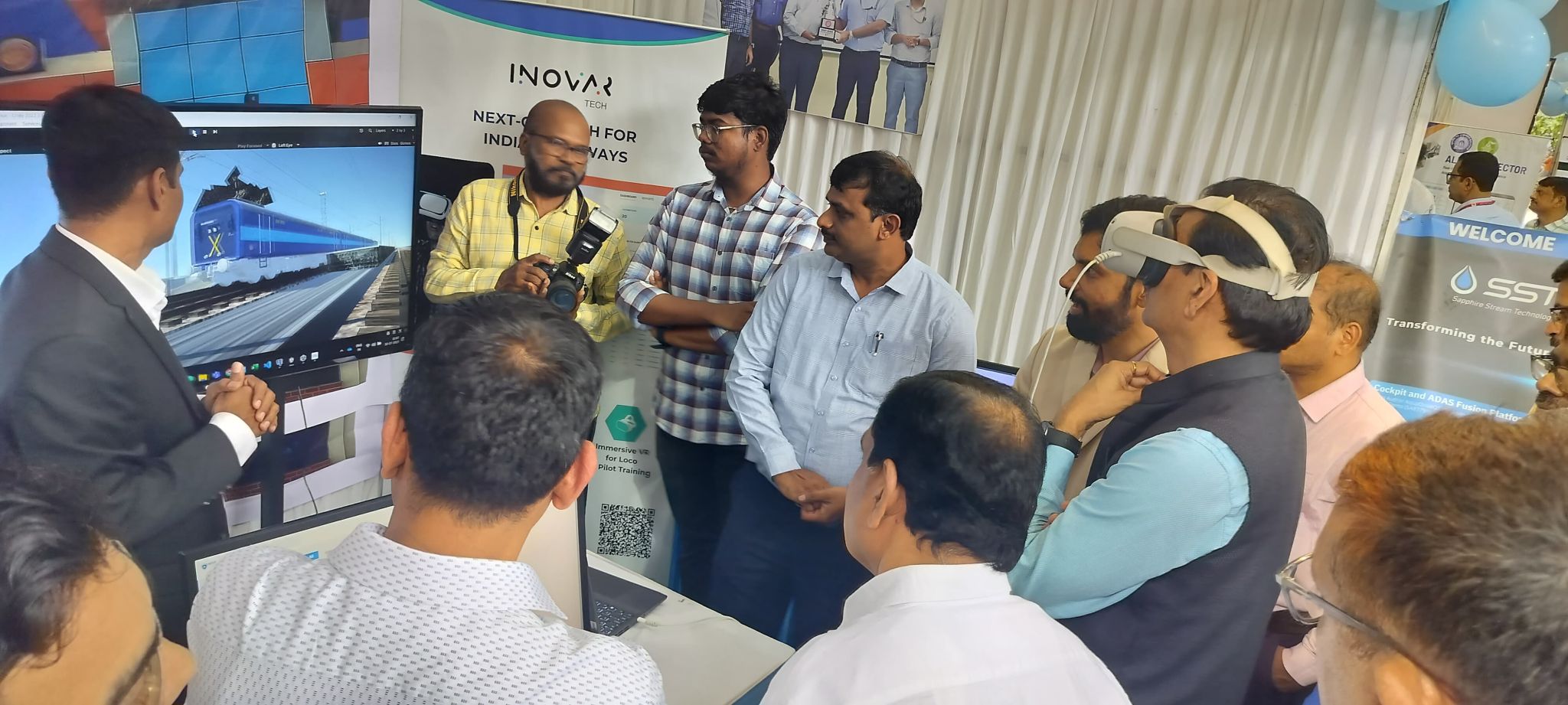





Key Interactions & System Behaviour
Scenario | Core Interaction | UX Consideration | Outcome |
Bogie Inspection | Kneel, pinch to rotate wheel set | Hand-tracking + teleport pivot | 93% task success |
Pantograph Isolation | Voice command “lock PT” + lever pull | Multimodal (voice + hand) | 22% faster than controller-only |
Emergency Brake Drill | Time-critical teleport to cab, pull master brake | Blink-based vignette during sprint to curb sickness | Zero nausea reports |
Results & Feedback
Metric (n = 42 trainees) | Traditional Class | VR Pilot | Δ |
Time to competency | 9 hrs | 5.8 hrs | –35% |
Assessment pass rate | 78% | 94% | +16 pp |
Reported engagement (1-5) | 3.1 | 4.6 | +48% |
Motion-sickness incidents | N/A | 7% | within comfort threshold |
Supervisors cited 30% fewer minor errors during live practise runs one month later, attributing gains to “muscle-memory realism.”
What I Learned
Design for Controller Diversity – Hand tracking plus voice reduces reliance on joysticks and boosts inclusivity for first-time VR users.
Progressive Disclosure Beats Full Fidelity – Layering information avoids overwhelming novices yet keeps technicians satisfied.
Motion Comfort Is Non-Negotiable – Teleportation and adaptive FOV together nearly eliminated sickness complaints in a population previously flagged as sensitive.
Stakeholder Co-creation Accelerates Adoption – Early demos to training officers secured buy-in and surfaced domain-specific terminology that improved UI labels.
More Projects
UI / UX Design
Training Smarter, Not Harder: Redesigning Onboarding for India’s Rail Engineers
Built a VR simulation using Meta Quest 2 that cut training time and made safety drills more real—without the risks
Year :
2025
Industry :
AR/VR
Client :
Indian Railways
Project Duration :
6 months



Project Summary
Indian Railways wanted to replace costly, travel-heavy classroom sessions with an immersive VR program that lets new engineers practise safety procedures and equipment handling in a lifelike but risk-free setting. I served as VR Experience Designer for a six-month pilot, partnering with a small squad of VR developers and railway domain experts. The result is a Quest 2-based simulation that blends gaze-driven teleport navigation, optional hand-tracking controls, structured tutorials, and real-time feedback to prepare recruits for real locomotives.



The Challenge
Cost & Scale – Training 1.5 lakh staff on physical simulators costs ₹350 cr and requires 47 decentralised centres.
Safety – Live drills around rolling stock expose novices to hazards such as high-voltage OHE lines and moving bogies.
Accessibility – Early user tests showed many trainees struggled with twin joysticks and long sessions triggered motion sickness.






My Role & Team
Responsibility | Contribution |
|---|---|
UX Strategy | Defined learning goals, success metrics, and interaction model |
Research Lead | Ran contextual inquiry inside training sheds and conducted 18 semi-structured interviews |
Interaction Design | Prototyped locomotion, menu, and feedback systems in Unity |
Usability Testing | Led three iterative play-tests with 28 participants |
I collaborated daily with two Unity developers, one 3D artist, and two senior training officers from the Kurla Car Shed.
User Research & Needs
Methods: field observation in maintenance sheds, think-aloud VR prototypes, and task analyses.
Key Insights
Low Controller Literacy – Only 22% of recruits had prior VR exposure; joystick “thumb drift” slowed task completion by 18 s on average.
Critical Recall Moments – Trainees must memorise sequences (e.g., pantograph isolation) under time pressure. Static videos failed to build muscle memory.
Motion Comfort – Continuous locomotion triggered nausea in >40% of novices; teleportation reduced adverse reports to 7%.
VR Design Approach
Locomotion & Navigation
Gaze-assisted teleportation with arc pointers keeps optical flow near zero to curb VR sickness.
Room-scale interaction inside engine compartments for tasks demanding fine manipulation (e.g., replacing brake pads).
Interaction Model
Hand-Tracking 2.2 on Quest 2 enables natural pinches and grabs for users who find controllers intimidating.
Context-sensitive affordances: interactive parts glow on proximity to reduce cognitive load.
Onboarding & Comfort
Five-minute guided tutorial introduces safety bubble boundaries, teleport mechanics, and comfort menu.
Dynamic vision modulator narrows peripheral FOV during rapid movement to mitigate motion sickness.
Accessibility toggles for seated mode, high-contrast UI, and language localisation (HI, EN).
Learning Progression
Observe – Cinematic 360° briefing.
Practise – Step-by-step scaffold with ghost-hand guidance.
Assess – Timed scenario without hints; scoring on accuracy, safety, and time.
Feedback Systems
Spatial audio cues for hazard warnings.
HUD badge meter tracking errors and remaining steps.
Post-scenario heat-map replay pinpointing missteps for instructor debriefs.






Key Interactions & System Behaviour
Scenario | Core Interaction | UX Consideration | Outcome |
Bogie Inspection | Kneel, pinch to rotate wheel set | Hand-tracking + teleport pivot | 93% task success |
Pantograph Isolation | Voice command “lock PT” + lever pull | Multimodal (voice + hand) | 22% faster than controller-only |
Emergency Brake Drill | Time-critical teleport to cab, pull master brake | Blink-based vignette during sprint to curb sickness | Zero nausea reports |
Results & Feedback
Metric (n = 42 trainees) | Traditional Class | VR Pilot | Δ |
Time to competency | 9 hrs | 5.8 hrs | –35% |
Assessment pass rate | 78% | 94% | +16 pp |
Reported engagement (1-5) | 3.1 | 4.6 | +48% |
Motion-sickness incidents | N/A | 7% | within comfort threshold |
Supervisors cited 30% fewer minor errors during live practise runs one month later, attributing gains to “muscle-memory realism.”
What I Learned
Design for Controller Diversity – Hand tracking plus voice reduces reliance on joysticks and boosts inclusivity for first-time VR users.
Progressive Disclosure Beats Full Fidelity – Layering information avoids overwhelming novices yet keeps technicians satisfied.
Motion Comfort Is Non-Negotiable – Teleportation and adaptive FOV together nearly eliminated sickness complaints in a population previously flagged as sensitive.
Stakeholder Co-creation Accelerates Adoption – Early demos to training officers secured buy-in and surfaced domain-specific terminology that improved UI labels.
More Projects
UI / UX Design
Training Smarter, Not Harder: Redesigning Onboarding for India’s Rail Engineers
Built a VR simulation using Meta Quest 2 that cut training time and made safety drills more real—without the risks
Year :
2025
Industry :
AR/VR
Client :
Indian Railways
Project Duration :
6 months



Project Summary
Indian Railways wanted to replace costly, travel-heavy classroom sessions with an immersive VR program that lets new engineers practise safety procedures and equipment handling in a lifelike but risk-free setting. I served as VR Experience Designer for a six-month pilot, partnering with a small squad of VR developers and railway domain experts. The result is a Quest 2-based simulation that blends gaze-driven teleport navigation, optional hand-tracking controls, structured tutorials, and real-time feedback to prepare recruits for real locomotives.



The Challenge
Cost & Scale – Training 1.5 lakh staff on physical simulators costs ₹350 cr and requires 47 decentralised centres.
Safety – Live drills around rolling stock expose novices to hazards such as high-voltage OHE lines and moving bogies.
Accessibility – Early user tests showed many trainees struggled with twin joysticks and long sessions triggered motion sickness.






My Role & Team
Responsibility | Contribution |
|---|---|
UX Strategy | Defined learning goals, success metrics, and interaction model |
Research Lead | Ran contextual inquiry inside training sheds and conducted 18 semi-structured interviews |
Interaction Design | Prototyped locomotion, menu, and feedback systems in Unity |
Usability Testing | Led three iterative play-tests with 28 participants |
I collaborated daily with two Unity developers, one 3D artist, and two senior training officers from the Kurla Car Shed.
User Research & Needs
Methods: field observation in maintenance sheds, think-aloud VR prototypes, and task analyses.
Key Insights
Low Controller Literacy – Only 22% of recruits had prior VR exposure; joystick “thumb drift” slowed task completion by 18 s on average.
Critical Recall Moments – Trainees must memorise sequences (e.g., pantograph isolation) under time pressure. Static videos failed to build muscle memory.
Motion Comfort – Continuous locomotion triggered nausea in >40% of novices; teleportation reduced adverse reports to 7%.
VR Design Approach
Locomotion & Navigation
Gaze-assisted teleportation with arc pointers keeps optical flow near zero to curb VR sickness.
Room-scale interaction inside engine compartments for tasks demanding fine manipulation (e.g., replacing brake pads).
Interaction Model
Hand-Tracking 2.2 on Quest 2 enables natural pinches and grabs for users who find controllers intimidating.
Context-sensitive affordances: interactive parts glow on proximity to reduce cognitive load.
Onboarding & Comfort
Five-minute guided tutorial introduces safety bubble boundaries, teleport mechanics, and comfort menu.
Dynamic vision modulator narrows peripheral FOV during rapid movement to mitigate motion sickness.
Accessibility toggles for seated mode, high-contrast UI, and language localisation (HI, EN).
Learning Progression
Observe – Cinematic 360° briefing.
Practise – Step-by-step scaffold with ghost-hand guidance.
Assess – Timed scenario without hints; scoring on accuracy, safety, and time.
Feedback Systems
Spatial audio cues for hazard warnings.
HUD badge meter tracking errors and remaining steps.
Post-scenario heat-map replay pinpointing missteps for instructor debriefs.






Key Interactions & System Behaviour
Scenario | Core Interaction | UX Consideration | Outcome |
Bogie Inspection | Kneel, pinch to rotate wheel set | Hand-tracking + teleport pivot | 93% task success |
Pantograph Isolation | Voice command “lock PT” + lever pull | Multimodal (voice + hand) | 22% faster than controller-only |
Emergency Brake Drill | Time-critical teleport to cab, pull master brake | Blink-based vignette during sprint to curb sickness | Zero nausea reports |
Results & Feedback
Metric (n = 42 trainees) | Traditional Class | VR Pilot | Δ |
Time to competency | 9 hrs | 5.8 hrs | –35% |
Assessment pass rate | 78% | 94% | +16 pp |
Reported engagement (1-5) | 3.1 | 4.6 | +48% |
Motion-sickness incidents | N/A | 7% | within comfort threshold |
Supervisors cited 30% fewer minor errors during live practise runs one month later, attributing gains to “muscle-memory realism.”
What I Learned
Design for Controller Diversity – Hand tracking plus voice reduces reliance on joysticks and boosts inclusivity for first-time VR users.
Progressive Disclosure Beats Full Fidelity – Layering information avoids overwhelming novices yet keeps technicians satisfied.
Motion Comfort Is Non-Negotiable – Teleportation and adaptive FOV together nearly eliminated sickness complaints in a population previously flagged as sensitive.
Stakeholder Co-creation Accelerates Adoption – Early demos to training officers secured buy-in and surfaced domain-specific terminology that improved UI labels.





